
A Deep Dive into World of Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking
Industrial stamping machines are indispensable tools in the realm of metalworking, offering precision, speed, and efficiency in shaping and cutting metal sheets into specific forms. These machines leverage high-pressure processes to perform various tasks such as punching, blanking, embossing, bending, and coining. Their application spans across numerous industries, from automotive to medical devices, making them essential in the production of consistent, high-quality metal parts. Despite their versatility, industrial stamping machines also face certain limitations, particularly regarding material constraints and the complexity of shapes they can produce. This blog will delve into the intricacies of 2024 Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking, their applications across different industries, and the challenges they encounter.
Introduction to Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking
A. How Industrial Stamping Machines Work
Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking function through a series of high-pressure operations. These processes include:
1. Punching: Removing a portion of the metal sheet to create holes or shapes.
2. Blanking: Cutting out specific shapes from the metal sheet, which becomes the finished part or a part of a larger assembly.
3. Embossing: Creating raised or recessed designs on the metal sheet, often for decorative or functional purposes.
4. Bending: Deforming the metal sheet into a desired angle or curve without breaking it.
5. Coining: Applying high pressure to the metal sheet to imprint detailed designs or smooth out surfaces.
B. Benefits of Using Industrial Stamping Machines
The advantages of using industrial stamping machines in metalworking include:
1. Efficiency: They allow for the rapid production of large volumes of parts.
2. Precision: These machines can achieve high levels of accuracy, ensuring uniformity in each part produced.
3. Cost-Effectiveness: Stamping machines reduce material waste and labor costs, making them economically beneficial for mass production.
C. Key Components of Industrial Stamping Machines
Understanding the core components of industrial stamping machines is crucial for grasping their functionality:
1. Press: The main structure that houses all the operational components.
2. Die: The tool that shapes the metal sheet, consisting of two parts—the punch and the die.
3. Feeder System: Automatically feeds metal sheets into the press, ensuring continuous operation.
4. Control System: Allows operators to program and monitor the machine’s operations for precision and safety.
Applications in Various Industries
A. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking plays a pivotal role in manufacturing essential components:
1. Car Body Panels: Stamping machines produce large, intricate panels for car exteriors, including doors, hoods, and fenders.
2. Engine Components: Precision-stamped parts are crucial for engine performance and reliability.
3. Structural Parts: The chassis and frame components are often stamped to ensure strength and durability.
B. Electronics Industry
The electronics industry relies on stamping machines for creating various metal components:
1. Metal Enclosures: Stamped metal enclosures protect electronic devices from damage and interference.
2. Connectors: High-precision connectors are essential for electrical connectivity in devices.
3. Heat Sinks: Efficient heat dissipation components are stamped for managing device temperatures.
C. Construction Industry
In construction, industrial stamping machines contribute to building and infrastructure projects:
1. Metal Frames: Stamped frames provide structural support for buildings and bridges.
2. Beams: Custom-stamped beams are tailored to specific construction requirements.
3. Custom Hardware: Unique metal hardware components are produced for various construction applications.
D. Consumer Goods
The production of consumer goods benefits significantly from industrial stamping machines:
1. Household Appliances: Stamped parts are integral to the manufacturing of refrigerators, washing machines, and other appliances.
2. Kitchenware: High-quality kitchen utensils and cookware are often produced through stamping.
3. Furniture Parts: Durable and aesthetically pleasing metal parts for furniture are created using stamping processes.
E. Medical Devices
The medical device industry demands precision and reliability, which stamping machines provide:
1. Precision Parts: Stamped parts are crucial for the functionality of medical equipment.
2. Surgical Instruments: High-quality surgical tools are manufactured through stamping to ensure precision and sterility.
3. Medical Equipment: Components for devices like MRI machines and hospital beds are produced using stamping techniques.
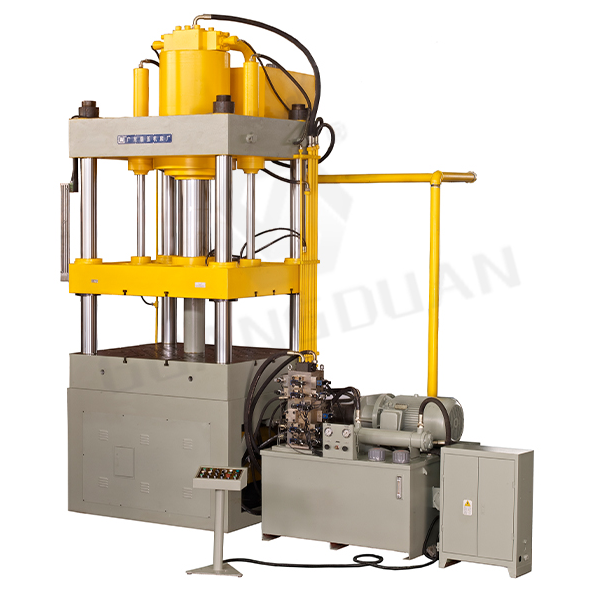

Limitations Within Metalworking
A. Material Constraints
While Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking is highly versatile, they do face limitations regarding the materials they can process:
1. Metal Specificity: They are most effective with metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper. Non-metal materials, such as plastics or composites, typically require different processing equipment.
2. Alloy Considerations: The performance of stamping machines can vary depending on the specific alloys used, affecting the final product’s quality.
B. Thickness Limitations
The effectiveness of stamping machines is often dictated by the thickness of the metal sheets:
1. Thin Metal Sheets: Stamping is particularly suited for thin metal sheets, allowing for precise and intricate designs.
2. Thicker Materials: When dealing with thicker materials, alternative methods such as forging or machining might be necessary due to the limitations in pressure and die capabilities.
C. Complexity of Shapes
While stamping machines excel at producing uniform parts, they can struggle with highly complex designs:
1. Intricate Designs: Extremely detailed and intricate shapes may be difficult to achieve solely through stamping and might require additional machining or finishing processes.
2. Tooling Costs: The cost of creating custom dies for complex shapes can be prohibitive, especially for low-volume production runs.
3. Secondary Operations: Additional processes, such as welding or assembly, might be required to achieve the final product’s desired complexity.
Common Problems in Metalworking
A. Material Waste
One of the significant issues in metalworking is material waste. Inefficient stamping processes can lead to:
1. Scrap Generation: Large amounts of scrap metal are produced if the stamping process is not optimized, leading to increased material costs.
2. Waste Management: Handling and recycling scrap metal can be costly and time-consuming, affecting overall production efficiency.
3. Resource Utilization: Inefficient use of raw materials impacts the environmental footprint and economic viability of metalworking operations.
B. Precision and Consistency
Achieving high precision and consistency in stamped parts is crucial, yet challenging due to:
1. Variations in Stamping Force: Inconsistent force application can result in parts with varying dimensions and quality.
2. Alignment Issues: Misalignment of dies and punches can lead to defective parts and increased scrap rates.
3. Quality Control: Ensuring every part meets stringent quality standards requires precise control over the stamping process.
C. Tool Wear and Tear
Frequent use of industrial stamping machines leads to:
1. Die Deterioration: Continuous high-pressure operations cause dies to wear out, reducing their effectiveness.
2. Punch Wear: Punches also suffer from wear and tear, impacting the quality of stamped parts.
3. Maintenance Needs: Regular maintenance is essential to keep the machines running efficiently, which can be time-consuming and costly.
D. Production Speed
Balancing high production speed with maintaining quality can be difficult:
1. Throughput Demands: Meeting high-volume production targets without compromising on quality requires efficient and reliable machines.
2. Downtime Reduction: Minimizing machine downtime for maintenance and repairs is crucial to maintaining production schedules.
3. Quality Assurance: Ensuring that rapid production does not lead to quality issues is a significant challenge.

Solutions Provided by Industrial Stamping Machines
A. High Efficiency
Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking offers high efficiency in production through:
1. Multiple Operations: Advanced machines can perform several operations in a single press cycle, reducing production time and increasing throughput.
2. Automated Processes: Automation in stamping processes enhances efficiency by reducing manual intervention and human error.
3. High-Speed Production: Modern stamping machines are capable of operating at high speeds, meeting production demands while maintaining quality.
B. Precision Engineering
To address issues of precision and consistency, industrial stamping machines are equipped with:
1. Precise Control Systems: Advanced control systems ensure accurate force application and alignment, resulting in consistent part quality.
2. Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the stamping process helps detect and correct issues promptly.
3. Quality Assurance: Integrated quality control mechanisms ensure that each part meets the required specifications and standards.
C. Material Optimization
Modern stamping techniques optimize material usage to minimize waste:
1. Progressive Die Stamping: This technique involves multiple operations in a single die setup, reducing scrap and optimizing material use.
2. Efficient Material Layout: Improved layout designs ensure maximum utilization of the metal sheet, reducing waste.
3. Scrap Reduction Strategies: Advanced machines incorporate strategies to minimize scrap, contributing to cost savings and sustainability.
D. Durability and Maintenance
Enhancements in machine durability and maintenance include:
1. Enhanced Die Materials: The use of stronger, more durable materials for dies and punches extends their lifespan and reduces wear.
2. Automated Maintenance Alerts: Modern machines feature automated alerts for maintenance needs, ensuring timely interventions and minimizing downtime.
3. Proactive Maintenance Programs: Implementing proactive maintenance schedules helps maintain production quality and extend the lifespan of machine components.

Conclusion
Industrial Stamping Machine for Metalworking is crucial in the metalworking industry, providing the ability to produce high-quality, consistent parts efficiently. Their applications span across various sectors, including automotive, electronics, construction, consumer goods, and medical devices. However, they do face limitations related to material constraints, the thickness of metal sheets, and the complexity of shapes they can produce. Manufacturers like GUANG DUAN continue to innovate, offering advanced and versatile machines that address these challenges and meet the evolving needs of the industry. As technology progresses, industrial stamping machines will likely become even more integral to metalworking and manufacturing processes, driving advancements in production capabilities and product quality.
CONTACT US

Guangdong Metal Forming Machine Works Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us



