-
Home / Forge Press
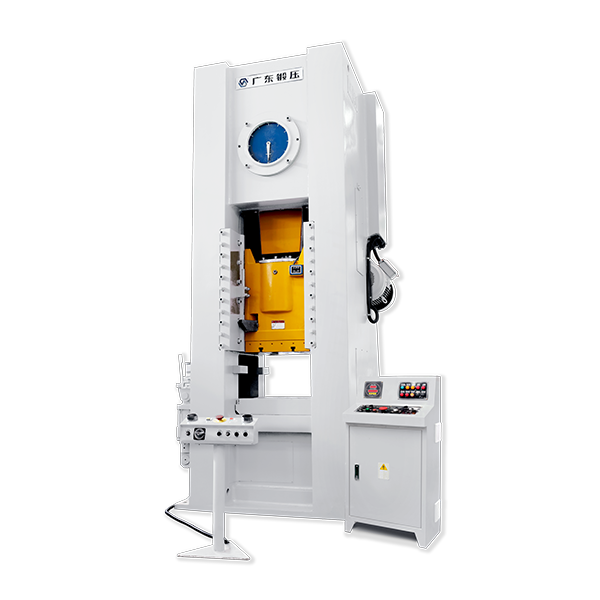
Forge Press
What is a Forge Press?
A forge press is a process that uses a vertical ram to apply gradual controlled pressure to a die holding a workpiece. The process is similar to drop forging but uses slow pressure instead of a series of blows. The slow movement of the ram penetrates deeper into the workpiece so that the workpiece undergoes uniform plastic deformationAdvantages of Forge Press
Strength to Weight Ratio
During the hydraulic forging press process, the grain structure of the piece becomes compressed, which creates reduced stress on the corners and fillets increasing the strength of the piece.Reduced Defects
Forging reduces metallurgical defects such as porosity and alloy segregation, which reduces the time for machining the completed piece and a positive response to heat treatment.Post Forging Treatments
With the absence of voids and porosity, pieces can be machined after forging without a loss of dimensional accuracy or quality. Tolerances are within 0.01 to 0.02 inches.Cost Savings
The saving factors for forging include raw material usage, reduced machining time, and reclamation of die material.Higher Productivity
Forging presses have a wide range of tonnage from several hundred to several thousand with working strokes per minute as high as 40 or 50, which is 40 to 50 parts per minute. Parts are completed in a single squeeze, which can be slowed by complex and intricate designs. The hydraulic forging press process can be used for mass production of nuts, bolts, rivets, screws, brake levers, bearing races, valves, and many other parts. Guangduan hot and cold forge presses are built for the most intensive applications in metal forming. Our wide range of forge presses can incorporate knuckle joint drives and link drives. This flexibility allows us to help you consistently achieve the perfect press production stroke for your most demanding jobs.The Comprehensive Guide to Forge Press
Forge press is an essential tool in the manufacturing industry, utilized for shaping metals through the application of force. Its versatility and efficiency have made it a staple in various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of forge press, understanding its numerous applications, types, advantages, and more.
Introduction to Forge Press
Forge press, an industrial machine, is designed to shape metals by applying force. It plays a vital role in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, as it allows manufacturers to produce complex metal parts with precision and efficiency. With its ability to work with various types of metals and alloys, forge press has become a must-have tool in today’s manufacturing landscape.
How Forge Press Works
The forge press operates by applying force to a heated metal workpiece, causing it to deform and take the shape of the die or mold. The process begins with heating the metal to a specific temperature, making it malleable and more comfortable to work with. Once heated, the metal is placed between the upper and lower dies, which are then pressed together, forcing the metal to take the shape of the die cavity.
Key Components of a Forge Press
A forge press typically consists of several key components, including:
- Frame: The frame is the central structure that houses all other components of the press. It provides stability and support during the forging process.
- Ram: The ram is the moving component of the press, responsible for applying force to the workpiece. It can either move vertically or horizontally, depending on the press design.
- Die: The die is the mold in which the workpiece takes its shape. Each die is custom-made to create a specific part or component.
- Bolster Plate: The bolster plate is a support structure that holds the lower die in place.
- Ejector: The ejector is a mechanism that helps remove the forged part from the die after the forging process is complete.
Types of Forge Press
There are several types of forge presses, each with its unique features and applications. Let’s take a closer look at the most common types.
Mechanical Forge Press
Mechanical forge presses use a motor-driven flywheel to store and transfer energy to the ram. They are characterized by their high speed and precision, making them suitable for mass production tasks. However, they are less flexible in terms of force control and can be less energy-efficient compared to other types of forge presses.
Hydraulic Forge Press
Hydraulic forge presses operate by using hydraulic fluid to transfer force from a motor to the ram. These presses offer greater force control and can apply constant pressure throughout the forging process, ensuring consistent part quality. They are also more energy-efficient than mechanical presses. However, their slower operating speeds can make them less suitable for high-volume production tasks.
Screw Forge Press
Screw forge presses utilize a rotating screw to transmit force from a motor to the ram. They are capable of applying high forces, making them ideal for heavy-duty forging tasks. However, their slower speeds and less precise force control can make them less suitable for intricate or high-precision applications.
Pneumatic Forge Press
Pneumatic forge presses use compressed air to transfer force from a motor to the ram. They are known for their rapid operation and minimal energy consumption, making them suitable for lightweight forging tasks. However, their lower force capabilities can make them less ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Applications of Forge Press
Forge press is used in various industries for a wide range of applications. Some of the most common ones include:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, forge press is used to manufacture various components like engine parts, transmission components, suspension parts, and brake systems. The ability to produce high-strength, lightweight, and intricate parts makes forge press a perfect fit for the automotive sector.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace components require precision and high strength-to-weight ratios. Forge press is employed to manufacture critical parts like turbine blades, engine components, and landing gear systems. The process ensures reliability and durability, essential factors for aerospace applications.
Construction Industry
The construction industry utilizes forge press to produce heavy-duty components such as excavator parts, crane components, and earthmoving equipment. The process’s ability to create high-strength and durable parts makes it ideal for the demanding construction environment.
Energy Industry
In the energy sector, forge press is used to manufacture components for power generation equipment, turbines, and drilling equipment. The process’s ability to create complex and high-strength parts makes it a perfect fit for the energy industry.
Advantages of Forge Press
Forge press offers several advantages over other metalworking processes like casting or machining. Some of the key benefits include:
Improved Strength
The forging process aligns the grain structure of the metal along the part’s shape, resulting in improved strength and durability. Forged parts are known for their high resistance to fatigue and impact loading.
Reduced Material Waste
Forge press is an efficient process that requires minimal material removal, resulting in reduced material waste. This not only lowers production costs but also contributes to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Enhanced Precision
Modern forge presses come with advanced control systems that ensure precise force application and accurate part dimensions. This makes it possible to produce complex and intricate parts with minimal post-forging operations.
Cost-effectiveness
Forge press can be a cost-effective manufacturing solution, especially for high-volume production tasks. The process’s speed, efficiency, and ability to produce high-quality parts contribute to its overall cost-effectiveness.
Forge Press Maintenance and Safety
Proper maintenance and safety measures are crucial for the efficient operation of a forge press. Some essential maintenance and safety tips include:
- Regular Inspection: Conduct routine inspections of the press components to identify any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- Safety Guards: Install safety guards around the press to protect operators from potential hazards.
- Operator Training: Ensure that operators are well-trained and familiar with the press’s operation, safety features, and maintenance procedures.
Choosing the Right Forge Press
Selecting the right forge press for your application involves considering several factors, such as:
- Force Requirements: Determine the force needed to forge the desired parts and choose a press with the appropriate force capacity.
- Speed Requirements: Consider the desired production speed and select a press that can meet your throughput requirements.
- Precision Requirements: Evaluate the precision required for your parts and choose a press with the necessary control capabilities.
- Budget Constraints: Consider your budget and select a press that offers the best value for your investment.
Conclusion
Forge press is a versatile and efficient manufacturing tool that has become indispensable in various industries. Understanding its types, applications, advantages, and maintenance requirements can help you make an informed decision when choosing the right forge press for your needs. Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, construction, or energy sector, forge press can provide the precision, strength, and cost-effectiveness your business needs to thrive.
CONTACT US

Guangdong Metal Forming Machine Works Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us




