
Crankshaft Forming Press Explained for Industrial Forging Engineers
In modern engine plants, a Crankshaft Forming Press is no longer viewed as just a heavy press on the forging line. It has become a strategic machine that largely determines whether crankshafts for automotive, marine, and power-generation applications can endure millions of cycles without failure. When a crankshaft breaks in service, the result is downtime, warranty cost, and reputational damage, so OEMs increasingly see the Crankshaft Forming Press as a quality-critical asset rather than only a source of tonnage.
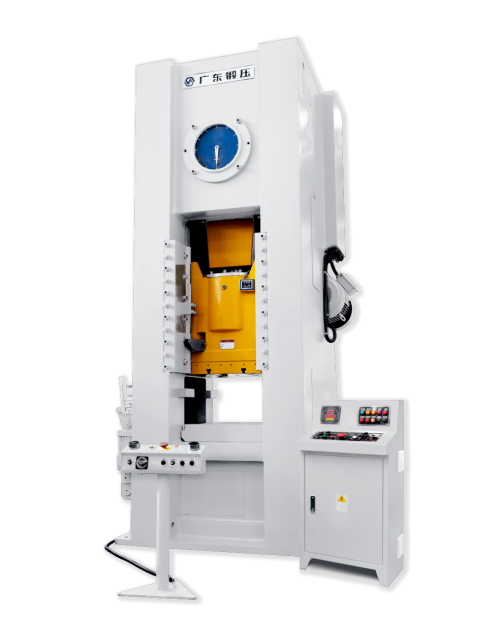

A dedicated Crankshaft Forming Press links billet temperature, material behavior, die life, automation, and cost per part. The press does more than apply force: it shapes grain flow, controls dimensions, and keeps output stable over long hot runs.
What Is a Crankshaft Forming Press?
A Crankshaft Forming Press is a closed-die forging press designed specifically to turn heated steel or alloy billets into near-net-shape crankshaft blanks. In just a few strokes it must distribute metal around offset crank throws, main journals, and fillets so that section thickness and fiber direction support high fatigue strength and good machinability.
Unlike a general-purpose forging press, a Crankshaft Forming Press is optimized for long, asymmetric workpieces that impose high bending loads on the frame and slide. Mechanical presses are often chosen for large, repeatable batch production, while hydraulic and servo-hydraulic presses provide finer control over stroke and force when producers need flexibility for larger crankshafts, new materials, or demanding fatigue and NVH requirements.
How the Forging Process Runs on a Crankshaft Forming Press
Production starts with billet heating and preparation. Billets must reach a narrow temperature window that provides plasticity without encouraging excessive grain growth or surface decarburization. If this step is unstable, defects such as folds, laps, and cracks tend to appear later in the line.
Preforming and blocking stages then redistribute material into the basic shape of journals, throws, and webs, usually over several die cavities. A Crankshaft Forming Press with a stable, repeatable stroke ensures that each preform cavity fills in a predictable way, which reduces variation and eases the load on the final impression. Final forming and sizing operations follow, defining main journals, crank pins, fillets, and webs. At this stage slide alignment and guidance have a direct influence on runout, concentricity, and machining allowances, while trimming and automated handling stabilize the forging as it cools.
Across all these stages, the behavior of the Crankshaft Forming Press shapes grain flow and mechanical properties. A stable press encourages grain orientation along the crankshaft’s load paths, helps minimize internal defects, and increases the likelihood that each forging will meet fatigue and dimensional targets without excessive rework.
Design Priorities for Modern Crankshaft Forming Presses
When plants specify new equipment or plan a line upgrade, nominal capacity is only the starting point. A modern Crankshaft Forming Press must provide enough forming energy for the longest crankshafts and highest-strength grades while also delivering high slide accuracy, reliable synchronization with manipulators and transfers, effective die protection, and thermal stability over long shifts.
GUANGDUAN designs Crankshaft Forming Press solutions with rigid frames, precise guidance, and fast-acting overload protection so that expensive dies and tooling are protected without sacrificing cycle time.
Structural Design and Core Components
In real-world production, structural weaknesses quickly drive up costs. A high-performance Crankshaft Forming Press is engineered with a high-rigidity box-type closed frame that evenly carries forging loads and keeps frame deflection under tight control. Such rigidity safeguards die parting-line alignment and helps metal flow fully into intricate crankshaft features. The drive system is commonly based on an eccentric-shaft crank design equipped with robust bearings and a wet-type clutch, delivering steady torque, progressive engagement, and long operating life. Precisely machined, four-side guideways secure the slide path, improving dimensional repeatability and reducing die wear. Mechanical die-height adjustment with a digital display simplifies die setup and speeds changeover between different crankshaft families.

Hydraulic overload protection reacts rapidly when abnormal loads occur, limiting structural damage and protecting the die set. Combined with strong die clamping and quick-change systems, these features reduce unplanned downtime and make the Crankshaft Forming Press a dependable center of an automated forging cell.
Automation, Control, and Data Integration
Modern crankshaft forging relies on automation and data, not just operator feel. GUANGDUAN configures its Crankshaft Forming Press with PLC-controlled logic to handle stroke selection, slide speed profiles, and key force values. Where applications call for finer process resolution, servo or pneumatic subsystems can be applied, especially when establishing process windows for new crankshaft designs. The integrated recipe management tools allow users to save complete settings for each crankshaft model and load them with a few commands, helping to cut setup time and avoid operator-related errors. Real-time monitoring of load, displacement, and temperature provides early warning of process drift and supports traceability, predictive maintenance, and continuous improvement of cycle time and energy consumption. Safety systems such as light curtains and interlocks, together with optional feeding, transfer, and uncoiling-leveling equipment, move billets and forgings safely while reducing manual handling around the hot line.
Long-Term Value With GUANGDUAN Crankshaft Forming Press Solutions
A purpose-built Crankshaft Forming Press offers clear gains in quality and cost. Grain flow follows the crank throws more naturally, internal defects and residual stress are reduced, and dimensional scatter shrinks. Users see lower scrap and rework rates, fewer die failures, and more stable customer quality once a dedicated press and structured process are in place.
GUANGDUAN combines high-rigidity structures, accurate guidance, and intelligent control to deliver Crankshaft Forming Press solutions matched to real production needs. Press capacity, slide size, and automation level can be tailored to specific crankshaft lengths, materials, and throughput targets. Integration support for feeding, handling, trimming, and safety turns the press into the stable core of an efficient forging line. For plants planning a new crankshaft project or upgrading an existing line, partnering with GUANGDUAN and selecting a dedicated Crankshaft Forming Press built around real production data helps secure long-term value: higher quality, less scrap, more predictable costs, and a stronger competitive position in demanding engine markets.
CONTACT US

Guangdong Metal Forming Machine Works Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us



